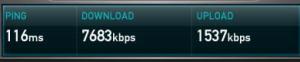
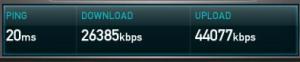
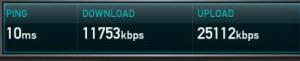
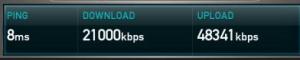
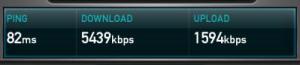
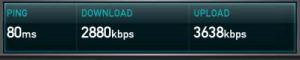
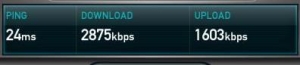
Hard as it may be to believe ADSL has been around in the UK for 10 years or so. In this time we have seen big changes in the industry. Market penetration has reached 58% of households (Ofcom 2008 review) and we are onto our third generation of technology.
Sebastien Lahtinen is known to many as the driving force behind thinkbroadband.com and before that ADSLguide.org.uk. As such he has been at the heart of the UK broadband industry as both an observer and participant since its beginnings.
TD Seb, tell us a bit about how you got into the broadband industry and what inspired you to originally found ADSLguide.org.uk
SL Back in the late nineties I was looking to get onto a cable broadband service but my cable operator Nynex (which became C&W, then NTL and now Virgin Media) wasn’t offering the service in my area. I then heard about this ‘ADSL’ technology and that Demon Internet was running trials in some areas. Whilst I couldn’t get onto a trial myself, John Hunt, a good friend of mine who started the site up with me was able to do so.
I felt that that there was a need for somewhere impartial for users to go, to find out about this new emerging technology. Of course these days, the providers have perfected their support and provisioning systems so our role has slightly changed. We now have to serve a far wider, less technical, user base.
TD ADSLguide.org.uk morphed into thinkbroadband.com. This was mainly because adsl was no longer the only driving technology in this space. Has this made a difference to how the website is perceived/used.
SL There are still people that consider us as an ‘ADSL’ site but we’re working hard to cover other broadband technologies including cable and mobile broadband. Our staff obviously understand the development and background of ADSL technology far better, but we are trying to build relationships with non-ADSL providers so we can offer users the best advice no matter what technology they want to use.
TD What makes thinkbroadband different to all the other comparison sites that now exist?
SL We don’t regard our site as a ‘comparison’ site in that we set it up to provide users with information about broadband generally, not just as a way comparing service providers. You can see this by comparing our front page which is more about news than trying to get you to switch service provider. Obviously, the ability to find a suitable supplier is part of what we do, but it’s by no means the primary role of the site.
The majority of the broadband sites out there (with ourselves and ISPreview.co.uk being obvious exceptions), were set up when service providers started offering commission for websites which referred a customer to them. In fact, this is the business model on which they operate. Some of them even compare insurance, credit cards, etc. as well.
Obviously, we have costs too and we need to ensure we can pay for those big servers that run the speed tests and to employ staff who can help to improve our site, but the major difference between us and most other sites, is we set the site up for the community, rather than as a business, and most of us are still doing this part time alongside full time jobs which pay our salaries.
TD The site has become very popular and this must put strain on your infrastructure. How did you manage the growth?
SL Around the same sort of time in early summer of 2000, I co-founded a hosting business with Jeremy Ainsworth who also got involved in ADSLguide. In fact, our very first server dedicated to serving ADSLguide was a spare box Jeremy had available which we put into Telehouse. We kept throwing more resources at it as it grew.
Our forums too gained their own momentum and we started seeing load issues when Pipex users took over the forums following some heated discussions about their service. David Rickards of Pipex was kind enough to donate a new server to us which helped us grow the forums to the next phase.
We started providing speed tests, and much more and our infrastructure had to grow with that. This is still very important to us to ensure we can deliver the fastest and most reliable speed test services.
TD Since that time what are the milestones that stick in your mind that measure the development of broadband in the UK
SL I think the first key milestone was when BT introduced the ‘wires only’ install which meant you didn’t have to use the ‘Alcatel frog’ (or ‘stingray’ as some people call it) with drivers that didn’t always work and the setup fee dropped from £150 to £50 making the service more universally affordable.
The second milestone I believe was BT’s “Broadband Britain” campaign which encouraged communities to get involved in raising broadband take-up and getting virtually all the exchanged enabled.
The third was the introduction of rate-adaptive ADSL and what we now know as the ‘up to 8 meg’ services. Since then, many other providers have started pushing the speed boundaries with LLU and especially recently Virgin Media on its 50 meg service too.
I believe the next challenge will be bringing those who are currently outside of broadband coverage into the digital world.
TD We are now seeing the Government talking about Universal Service Obligation concerning the provision of 2Mbps broadband to all homes. Do you believe this is practical?
SL We do believe that a USO is absolutely necessary and that the level at which it is set should be reviewed regularly. Our current concern is more for those who cannot get any broadband service, than those who are stuck on say 1Mbps services, as this is a far more fundamental problem that needs to be dealt with as a matter of urgency. I could probably survive on a 1Mbps connection, but I can’t imagine living ‘without broadband’ at all.
We also have some doubts as to whether it is possible to simplify a USO as just “2Mbps downstream” service. There are factors such as upstream speed, latency, jitter, etc. that could for example prevent access to next generation telephony service over the Internet which have the potential to revolutionise how we communicate. These don’t make as interesting a sound bite but they are still important.
TD As the internet becomes more important to our every day lives the Government is increasingly seen as becoming involved with decisions that affect the direction of the industry. Do you see this as good or bad and is it inevitable? What are your thoughts on the Digital Britain Report?
SL The Government has an important role in ensuring a regulatory environment which both fosters innovation and diversity of supply, but also protects those who may not have the resources or skills to protect themselves. However, it is important, that in achieving the latter, it does not stifle the former.
The Internet has developed in an environment with very minimal regulation and low barriers to entry, and it is these unique circumstances that have allowed it to develop so quickly. The Internet feeds on the concept of rapid innovation and improvement. One day you launch a brilliant new service; the next, your competitor has outdone you. It’s a bit like a car manufacturer being able to release a new updated model every week.
The way we think and use information since the evolution of the web has changed. We now combine information from different sources in new ways. This is only possible if those with an idea have the means and willingness to execute it. It does however mean re-thinking the way intellectual property rights are protected, both to preserve the incentive for those who work hard to benefit from their efforts, but also to allow for people to take advantage of new technologies without being criminalised.
In my view, the role of the Government is to encourage good practice and getting directly involved only where it is absolutely necessary to protect the interests of the country and its economy. So far, the UK Government has taken a ‘light touch’ approach which has helped us become a key capital at the heart of the Internet.
I suspect that Government will become more involved in the discussion about the future of the Internet as it is so fundamentally linked to the success of the country and the Digital Britain report is evidence of this. We also have to accept that there is a role for an entity to represent the interests of the minority who are unable to use the Internet for whatever reason. It is no longer sufficient for us to cover 99.9%; The Internet should be for everyone.
TD We now hear of talk of 1Gbps fibre to the home in Japan which doesn’t even appear on the long range radar here in the UK. How do you think the UK will fare in the international competitive stakes when it comes to internet technology.
SL The UK has a habit of comparing itself to other countries and being very negative about its position. The fact is, there is very little content on the Internet which can truly benefit from a 100Mbps let alone a 1Gbps connection today. Quite simply, the core Internet infrastructure can’t cope with delivery this level of service on any scale at a price that most of us would be willing to pay.
I do however have concerns that we aren’t looking at a national fibre network more seriously. Whilst I accept that the needs of the next few years will be met by new ways to push more out of copper (both in ADSL and cable variants) and hybrid fibre-coax/copper solutions, sooner or later end-to-end fibre optic cabling will be needed and it is likely that this will require Government support by way of easing regulation or co-ordinating the efforts of communications providers to build an efficient and competitive network.
The reason fibre makes sense is because information travels along it at the speed of light so its capacity to deliver next generation services is far greater. The fibre optic cabling used to deliver 100Mbps or 1Gbps a decade ago is used to push multiple links of 10Gbps each today and 100Gbps in the not too distant future. It is a technology that is more future-proof than copper.
TD Finally would you care to make any predictions regarding the internet in the UK over the next year or two?
SL I think we will start seeing more new developments receiving next generation broadband services at up to 100Mbps in cities as the costs of linking these back to the data centres (the buildings where the ‘core’ of the Internet is based) is falling.
I also believe that the the much talked about convergence of technologies will start happening, initially with TV-on-demand services being delivered over the Internet to your set-top-box. Eventually (probably a few years later), I think Internet-connected fridges are likely to become more common.
TD Thanks very much for your time Seb.
 EE is doing a good job at building up market expectation. Today the mobile network operator launched its pricing plans, available from the end of this month.
EE is doing a good job at building up market expectation. Today the mobile network operator launched its pricing plans, available from the end of this month.